The collection of functional cardiovascular endpoints, such as ECG and blood pressure, are most commonly achieved using Jacketed External Telemetry (JET™), Implantable Telemetry, or Hardwired Instrumentation.
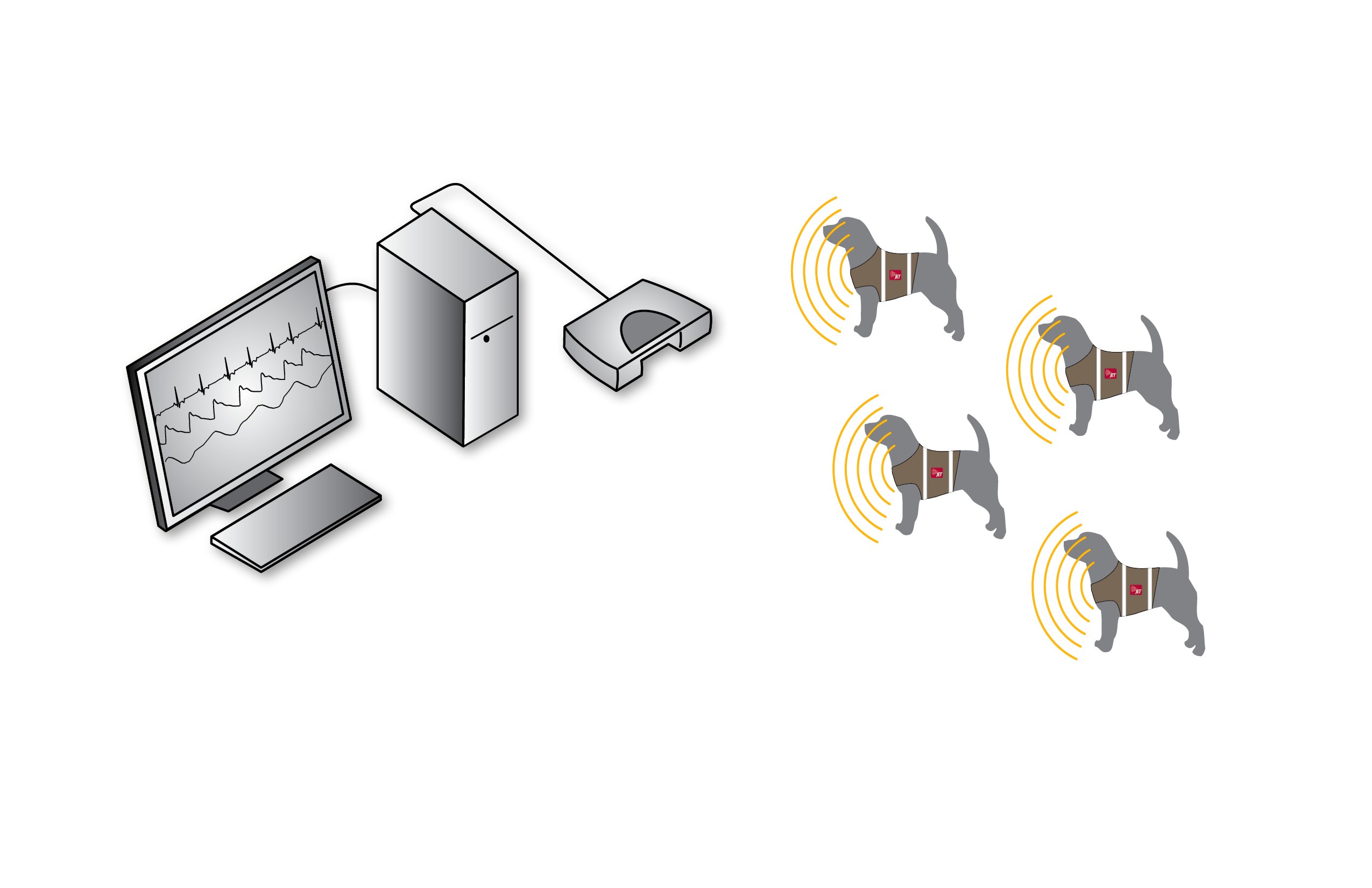
Jacketed External Telemetry
Functional endpoints are collected from conscious, freely moving animals wearing a jacket that contains and protects a small JET device capable of monitoring cardiovascular data and transmitting data to an acquisition and analysis computer system.
ECG data are collected via the placement of electrodes on the exterior of the animal that are connected to the JET Device. Numerous derived endpoints are available from the ECG but the most commonly evaluated are Heart Rate, RR Interval, and the QT Interval with associated corrections.
Blood pressure data are collected via the placement of a Minimally Invasive Blood Pressure (MIBP) implant in an artery of the animal. This implant then transmits to a small antenna connected to the JET Device. The most commonly evaluated endpoints are systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures, pulse rate, and pulse pressure.
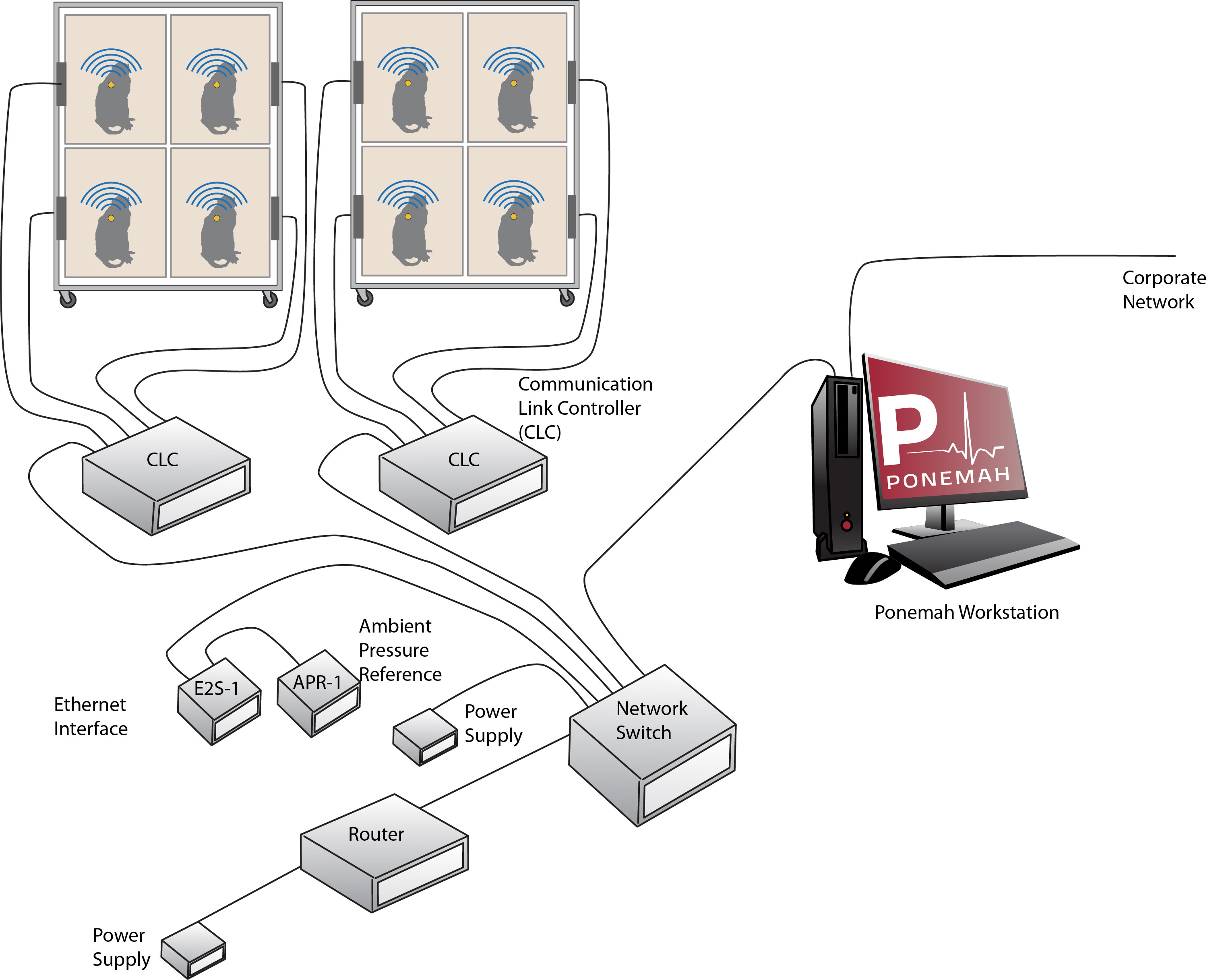
Implantable Telemetry
Functional endpoints are collected from conscious, freely moving animals that have a small device implanted into them that is capable of monitoring ECG, Blood Pressure, Temperature, and Activity data and transmitting data to an acquisition and analysis computer system.
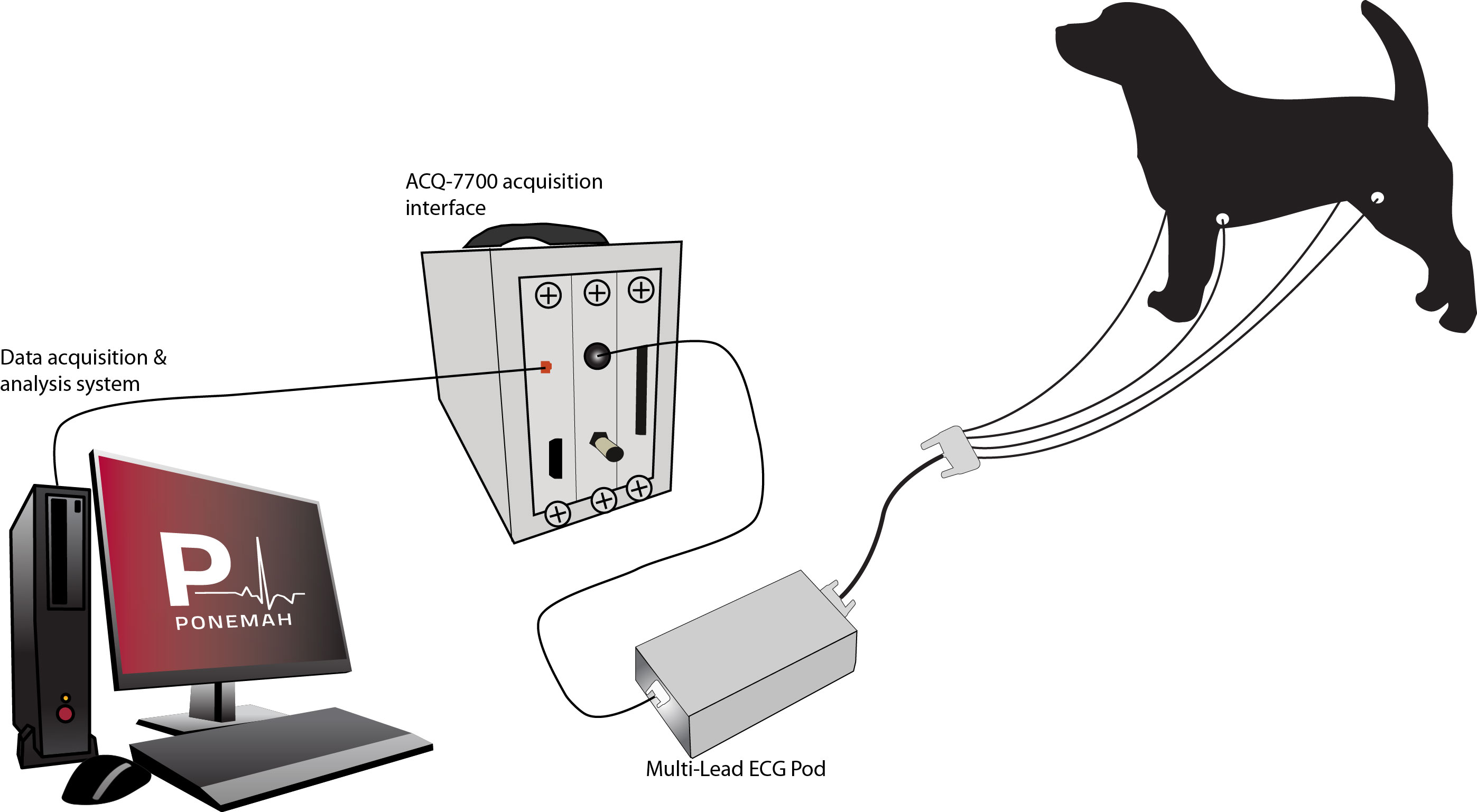
Hardwired Instrumentation
Short durations of functional endpoints are collected from chemically or physically restrained animals that are connected to external devices capable of monitoring ECG and recording directly into an acquisition and analysis computer system.